#include<opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include<opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include<opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
void main()
{
Mat Scr1 = imread("K:\\test.png");
Mat Scr2 = imread("K:\\test.png");
Mat Scr3 = imread("K:\\test.png");
if (Scr1.empty())
{
return;
}
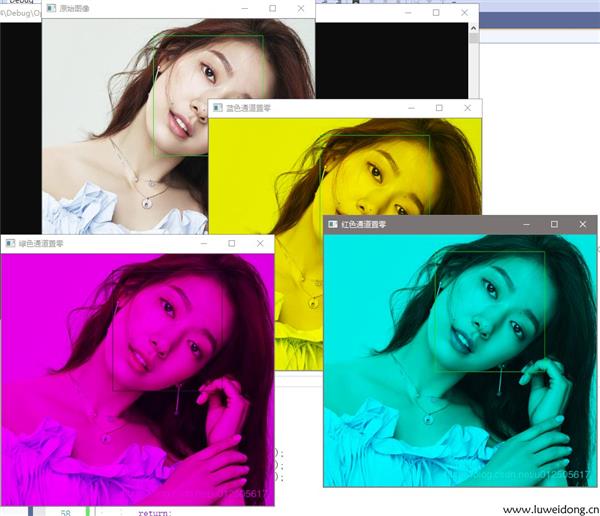
imshow("原始图像", Scr1);
//OpenCV中通道的顺序是BGR
int Row = Scr1.rows; //获取行数目
int Col = Scr1.cols; //获取列数目
int Channel = Scr1.channels(); //获取通道数目
//指针的访问
for (int i = 0; i < Row; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < Col; j++)
{
Scr1.ptr<Vec3b>(i)[j][0] = 0;
}
}
imshow("蓝色通道置零", Scr1);
//迭代器访问,访问的是每一个像素点
Mat_<Vec3b>::iterator it = Scr2.begin<Vec3b>();
while (it != Scr2.end<Vec3b>())
{
//(*it)[0] = 0;//蓝色通道置零;
(*it)[1] = 0;//绿色通道置零;
//(*it)[2] = 0;//红色通道置零;
it++;
}
imshow("绿色通道置零", Scr2);
//动态访问,访问的是每一个像素点,最慢也是最直接易理解的访问方式
for (int i = 0; i < Row; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < Col; j++)
{
Scr3.at<Vec3b>(i, j)[2] = 0;
}
}
imshow("红色通道置零", Scr3);
waitKey(0);
system("pause");
return;
}